Introduction
Forex brokers play a crucial role in the foreign exchange market, providing individuals and institutions with access to trade currencies. While many people are aware of the services offered by forex brokers, they may wonder how these brokers make their money. In this article, we will explore the various ways forex brokers generate revenue and the factors that contribute to their profitability.
Spread
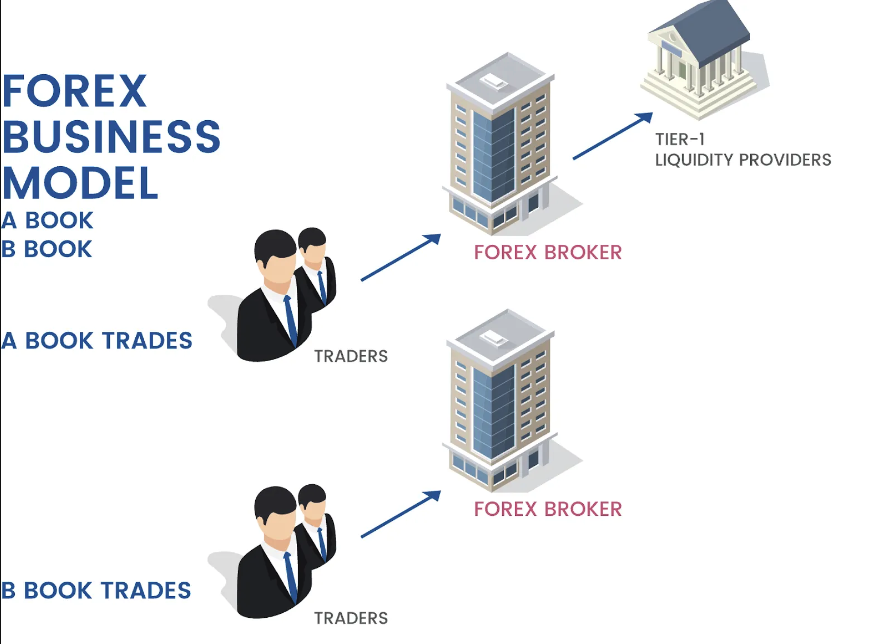
One of the primary ways forex brokers make money is through the spread. The spread refers to the difference between the buy and sell price of a currency pair. When you open a trade, you will notice that the price you buy at is slightly higher than the price you can sell at. This difference is the spread, and it represents the broker’s commission.
Forex brokers typically offer two types of spreads: fixed and variable. Fixed spreads remain constant regardless of market conditions, while variable spreads fluctuate based on factors such as market liquidity and volatility. In either case, the broker earns a profit by pocketing the difference between the buy and sell price.
It’s important to note that the spread can vary significantly between different currency pairs and brokers. Major currency pairs such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD tend to have lower spreads due to their high trading volume, while exotic currency pairs may have wider spreads.
Commissions
In addition to earning money through the spread, forex brokers may also charge commissions on trades. While not all brokers implement this fee structure, it is common among certain types of trading accounts, such as ECN (Electronic Communication Network) accounts.
ECN brokers connect traders directly to the interbank market, where they can access liquidity from various financial institutions. These brokers charge a commission for each trade executed, which is typically calculated as a fixed fee per lot traded. The commission-based model ensures that the broker earns a profit regardless of the spread.
Commissions can vary widely depending on the broker and the trading account type. Some brokers may offer lower spreads but higher commissions, while others may have higher spreads and lower or no commissions. Traders should consider their trading style and preferences when choosing a broker with a commission-based fee structure.
Swap Fees
Forex brokers also generate revenue through swap fees, also known as overnight financing charges. When you hold a position overnight, you are essentially borrowing one currency to buy another. As a result, the broker may charge or pay you interest for holding the position beyond the market close.
The swap fee is calculated based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies in the currency pair you are trading. If you are trading a currency with a higher interest rate against a currency with a lower interest rate, you may receive a positive swap, meaning the broker pays you. Conversely, if you are trading a currency with a lower interest rate against a currency with a higher interest rate, you may incur a negative swap, and the broker charges you.
Swap fees can vary depending on the broker and the currency pair being traded. Traders who frequently hold positions overnight should consider the swap fees when evaluating the overall cost of trading with a particular broker.
Additional Services and Upgrades
While the primary sources of revenue for forex brokers are spreads, commissions, and swap fees, some brokers offer additional services and upgrades that can generate extra income. These services may include:
- Managed Accounts: Some brokers offer managed accounts where experienced traders manage the funds on behalf of clients. In return, the broker charges a management fee or a percentage of the profits.
- Education and Training: Brokers may provide educational resources, webinars, and training courses for traders. These services may be offered for free or at a cost, generating revenue for the broker.
- Research and Analysis: Some brokers offer market research, analysis, and trading signals to assist their clients in making informed trading decisions. These services may be provided as part of a premium account or offered at an additional cost.
- Trading Tools: Brokers may develop and offer proprietary trading tools, such as advanced charting software, indicators, and expert advisors. These tools can enhance the trading experience for clients and may be offered as part of a premium package or sold separately.
These additional services and upgrades allow brokers to diversify their revenue streams and cater to the varying needs of traders. However, it’s important for traders to carefully evaluate the costs and benefits of these offerings to ensure they align with their trading goals and strategies.
Conclusion
Forex brokers make their money through various revenue streams, including spreads, commissions, swap fees, and additional services. The spread, which represents the difference between the buy and sell price of a currency pair, is the primary source of income for most brokers. Commissions are charged by some brokers, particularly those offering ECN accounts, while swap fees are incurred when holding positions overnight. Additionally, brokers may offer additional services and upgrades to generate extra income. Traders should consider these factors when choosing a forex broker and assess their impact on their trading costs and overall trading experience.



Leave a Review