Understanding Market Maker Brokerage
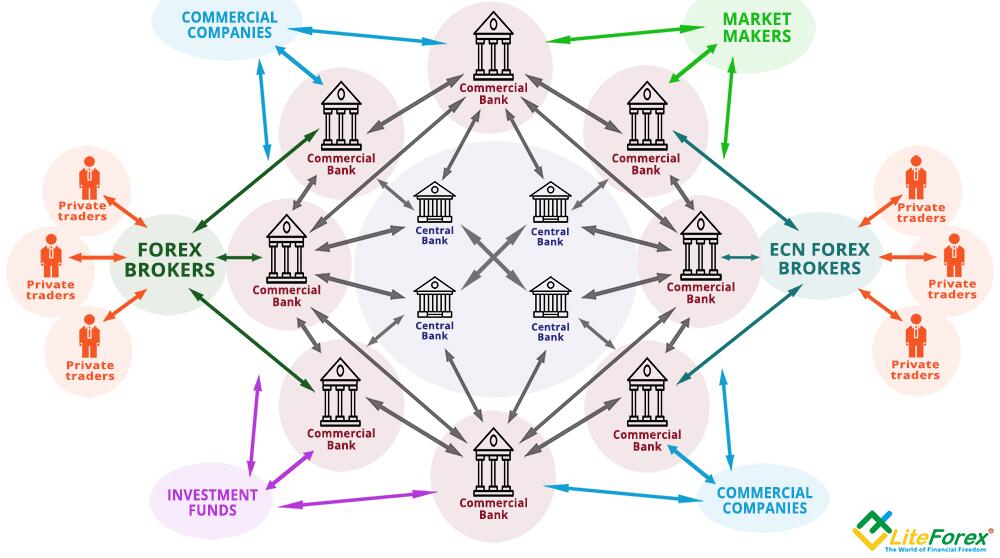
A market maker brokerage is a type of financial institution that facilitates trading in financial instruments by providing liquidity to the market. Market makers are responsible for maintaining an orderly and efficient market by quoting both buy and sell prices for a particular security or asset. They play a crucial role in ensuring that there is a continuous supply and demand for securities, which helps to facilitate smooth trading.
How Market Maker Brokerages Work
Market maker brokerages act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers in the financial markets. They typically hold an inventory of securities and are always ready to buy or sell those securities at a quoted price. This means that market makers are always willing to buy securities from sellers or sell securities to buyers, even when there is no immediate buyer or seller in the market.
When a trader wants to buy or sell a security, they can place an order with a market maker brokerage. The market maker will then execute the trade by either buying the security from the trader or selling it to them from their inventory. The market maker makes a profit by buying securities at a lower price and selling them at a slightly higher price, known as the bid-ask spread.
Market maker brokerages make money through the bid-ask spread and by charging commissions or fees on trades. The bid price is the price at which the market maker is willing to buy a security, while the ask price is the price at which they are willing to sell it. The difference between the bid and ask prices represents the market maker’s profit margin.
The Role of Market Maker Brokerages in the Market
Market maker brokerages play a crucial role in maintaining liquidity and stability in the financial markets. By always being willing to buy or sell securities, they provide liquidity to the market, ensuring that there is always a counterparty available for traders to transact with. This helps to prevent large price swings and allows for efficient price discovery.
Market makers also help to narrow the bid-ask spread, which is the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept. By quoting both buy and sell prices, market makers reduce the spread, making it easier and more cost-effective for traders to buy and sell securities.
In addition to providing liquidity, market maker brokerages also act as market participants, taking on risk in the process. They are constantly exposed to the possibility of adverse price movements and must manage their inventory and positions accordingly. Market makers use sophisticated trading algorithms and risk management techniques to ensure that they can fulfill their obligations and maintain a balanced book.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Market Maker Brokerages
Market maker brokerages offer several advantages to traders and investors:
- Liquidity: Market makers ensure that there is always a buyer or seller available in the market, making it easier to buy or sell securities.
- Tight Spreads: Market makers help to narrow the bid-ask spread, reducing transaction costs for traders.
- Fast Execution: Market makers can execute trades quickly, ensuring that orders are filled promptly.
- Price Stability: By providing liquidity and narrowing spreads, market makers help to maintain price stability in the market.
However, there are also some potential disadvantages associated with market maker brokerages:
- Conflict of Interest: Market makers may have a conflict of interest as they profit from the bid-ask spread and may not always have the best interests of traders in mind.
- Price Manipulation: In some cases, market makers may engage in price manipulation to benefit their own positions.
- Limited Transparency: Market makers may not always provide full transparency regarding their pricing and execution practices.
Conclusion
Market maker brokerages play a vital role in the financial markets by providing liquidity, maintaining price stability, and facilitating efficient trading. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, ensuring that there is always a counterparty available for transactions. While market maker brokerages offer advantages such as liquidity and tight spreads, traders should also be aware of potential conflicts of interest and limited transparency. Understanding how market maker brokerages work can help traders make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the financial markets.





Leave a Review